




Non-Laminated Magnetic Graph Board 120cm x 120cm (4ft x 4ft)
KSh7,500.00 Original price was: KSh7,500.00.KSh7,000.00Current price is: KSh7,000.00.

Office Document Tray - 3 Tier
KSh2,000.00 Original price was: KSh2,000.00.KSh1,799.00Current price is: KSh1,799.00.
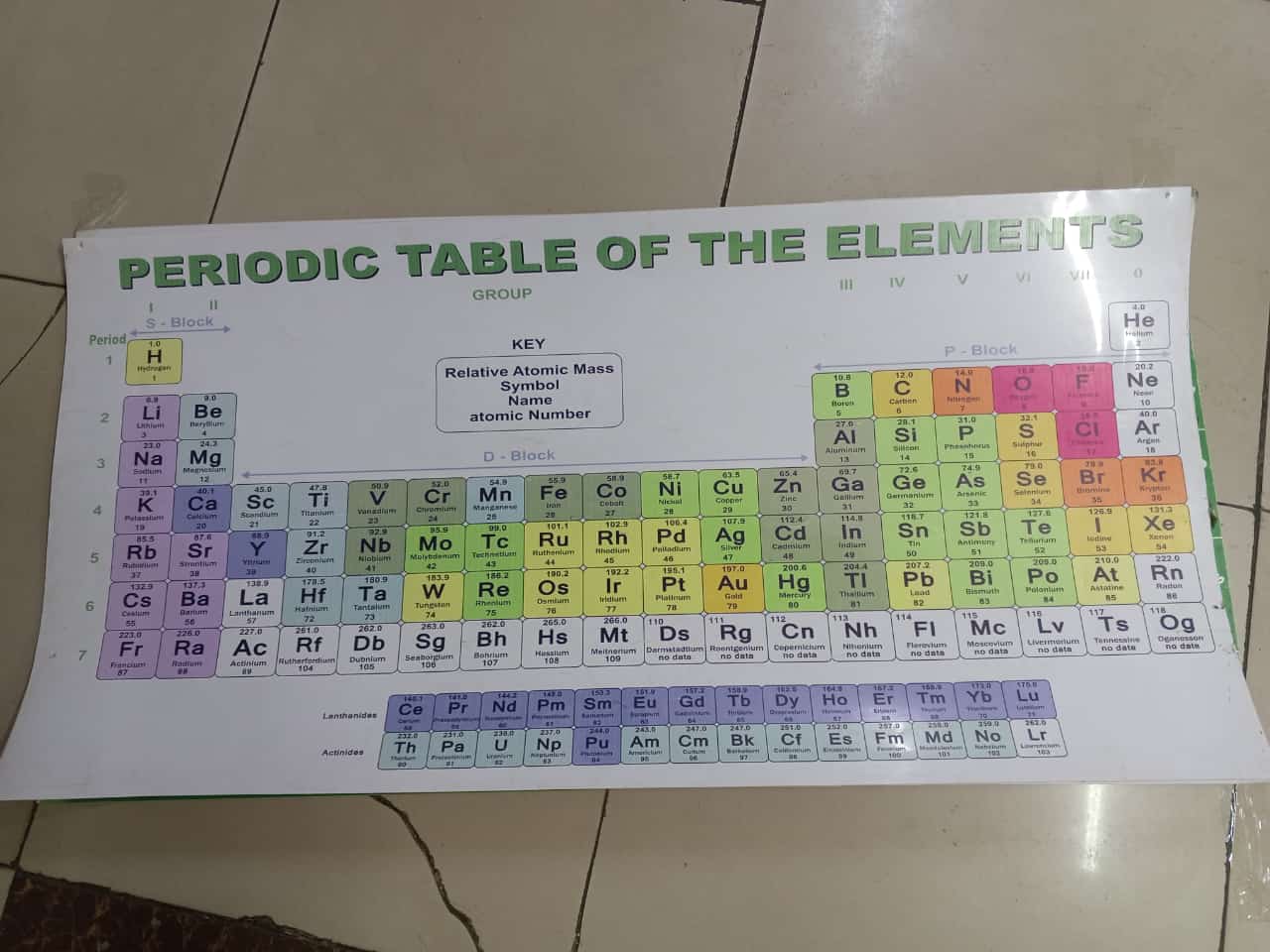
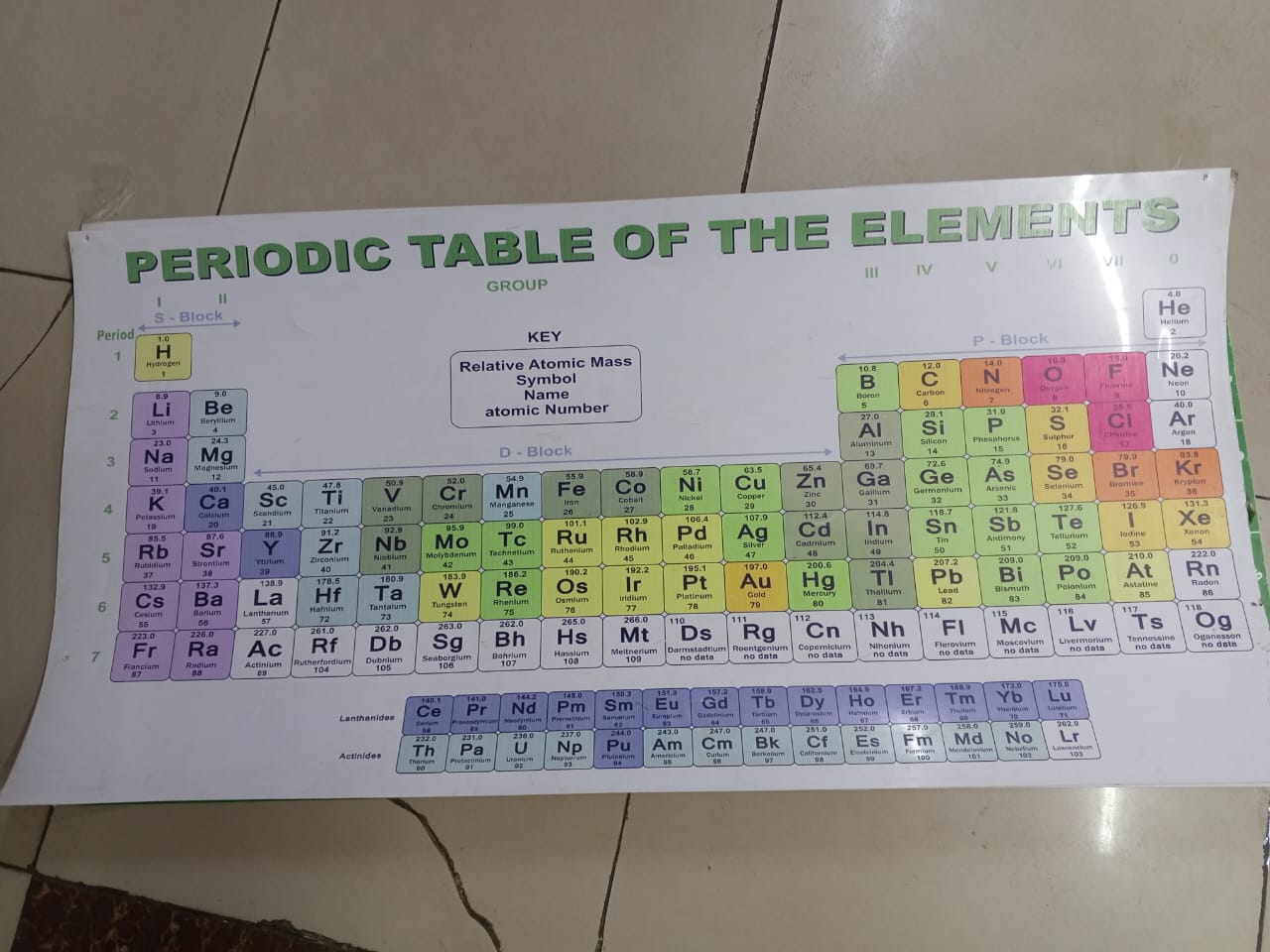
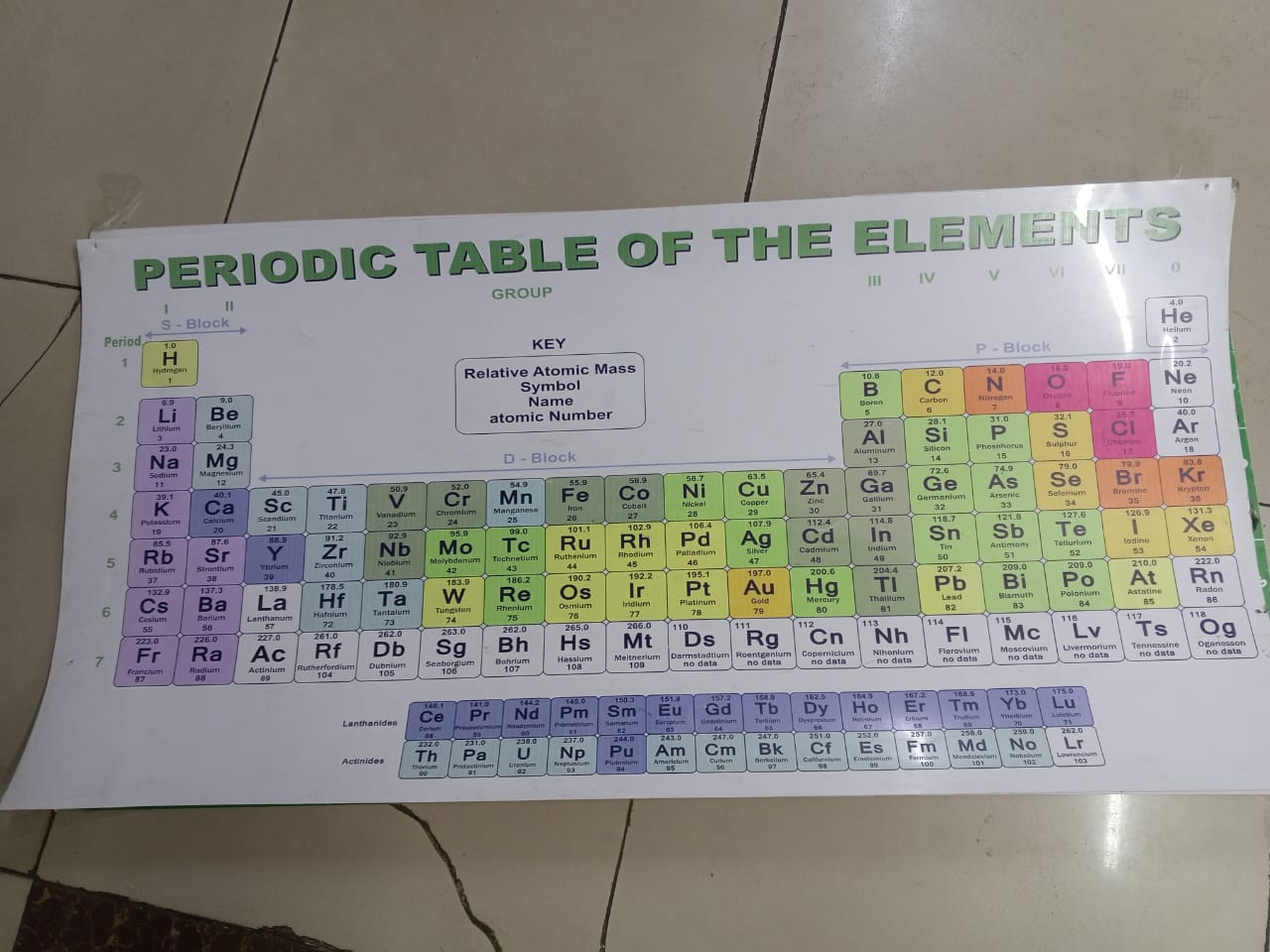
Periodic Table 4Ft x 2Ft
KSh10,000.00 Original price was: KSh10,000.00.KSh9,500.00Current price is: KSh9,500.00.
Description
It is a systematic arrangement of chemical elements, organized by increasing atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. It has arranged elements based on their atomic masses and noticed repeating patterns, or periodicity, in their properties. Modern versions of the table are based on atomic number rather than atomic mass.
Elements in the periodic table are arranged in rows called periods and columns called groups or families. Elements in the same group often exhibit similar chemical behaviors due to having the same number of valence electrons. For instance, alkali metals in Group 1 are highly reactive, especially with water, while noble gases in Group 18 are inert.
The table is divided into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Metals, found on the left and center, are typically shiny, conductive, and malleable. Nonmetals, on the right, are more variable in appearance and are poor conductors. Metalloids have properties between metals and nonmetals.
The periodic table is essential in chemistry and related sciences, helping predict element behavior, compound formation, and guiding research. It remains one of the most valuable tools for understanding matter at the atomic level.
Additional information
| Weight | 2 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 120 × 60 cm |
Shipping & Delivery


Delivery & Shipping
Delivery & Shipping charges will depends with distance and weight of the product.
Related products
3Ft x 2Ft PVB White Abyed Glass Board 10mm With Installation Studs
40cm x 40cm Canvas Board
Advertising Programmable LED Signage
- If your business is competing for attention in a busy area bright signage will help you get noticed. LED technology has advanced the ways in which your signs can be lit - from 3D fabricated letters, backlit logos and under awning lightboxes we will craft you the perfect sign.
- We specialise in genuine custom made neon signs, neon lights and neon art designed and manufactured using glass. We are passionate about producing a wide range of high quality neon products.
- With a genuine love of creating unique, one-off neon products, we believe our attentive approach sets us apart from our competitors, and we are dedicated to developing the ways in which neon is used, putting a modern twist on a product that has stood the test of time.
Black Board- Modern Alluminium framed durable 240cm x 120cm (8ft x 4ft)
CBC Modern Career Wheel Sheet 120cm x 120cm (4ft x 4ft)
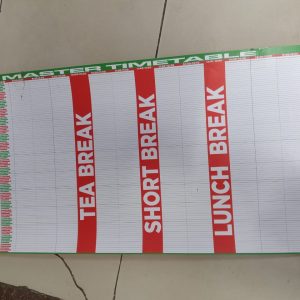
Master Timetable 4Ft x 2Ft
Office Desk & Chair 90cm x 56cm
Modern office furniture blends functionality with aesthetics, offering styles that suit various office environments?from minimalist designs to more traditional setups. With the increasing popularity of remote work, demand for ergonomic desks and chairs has grown, leading to more innovations such as sit-stand desks and chairs with enhanced mobility.
Programmable LED Signage For Sale
- If your business is competing for attention in a busy area bright signage will help you get noticed. LED technology has advanced the ways in which your signs can be lit - from 3D fabricated letters, backlit logos and under awning lightboxes we will craft you the perfect sign.
- We specialise in genuine custom made neon signs, neon lights and neon art designed and manufactured using glass. We are passionate about producing a wide range of high quality neon products.
- With a genuine love of creating unique, one-off neon products, we believe our attentive approach sets us apart from our competitors, and we are dedicated to developing the ways in which neon is used, putting a modern twist on a product that has stood the test of time.








 DOUBLE SIDED WHITEBOARD
DOUBLE SIDED WHITEBOARD DRY ERASE WHITEBOARD
DRY ERASE WHITEBOARD FREE STANDING WHITEBOARD
FREE STANDING WHITEBOARD MAGNETIC DRY ERASE WHITEBOARD
MAGNETIC DRY ERASE WHITEBOARD Flipchart Stand
Flipchart Stand FLIP CHART WITH WHEELS
FLIP CHART WITH WHEELS
 Non magnetic glass board
Non magnetic glass board
 FREE STANDING NOTICEBOARD
FREE STANDING NOTICEBOARD GLASS SLIDING NOTICEBOARD
GLASS SLIDING NOTICEBOARD INDOOR LOCKABLE NOTICEBOARD
INDOOR LOCKABLE NOTICEBOARD OUTDOOR LOCKABLE NOTICEBOARD
OUTDOOR LOCKABLE NOTICEBOARD PIN NOTICE BOARD
PIN NOTICE BOARD